Definition: The device which takes electrical energy is known as the electric load. In other words, the electrical load is a device that consumes electrical energy in the form of the current and transforms it into other forms like heat, light, work, etc. The electrical load may be resistive, inductive, capacitive or some combination between them. The term load is used in the number of ways.
- To indicates a device or a collection of the equipment which use electrical energy.
- For showing the power requires from a given supply circuit.
- The electrical load indicates the current or power passing through the line or machine.
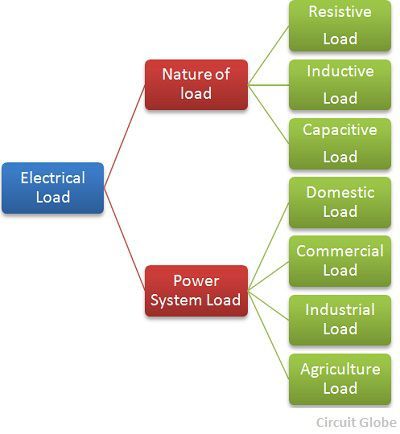
The classifications of loads are shown in the figure below.
Types of Electrical Loads
The nature of the load depends on the load factor, demand factor, diversity factor, power factor, and a utilisation factor of the system. The different types of load are explained below in details.
Resistive Load
The resistive load obstructs the flow of electrical energy in the circuit and converts it into thermal energy, due to which the energy dropout occurs in the circuit. The lamp and the heater are the examples of the resistive load. The resistive loads take power in such a way so that the current and the voltage wave remain in the same phase. Thus the power factor of the resistive load remains in unity.
Inductive load
The inductive loads use the magnetic field for doing the work. The transformers, generators, motor are the examples of the load. The inductive load has a coil which stores magnetic energy when the current pass through it. The current wave of the inductive load is lagging behind the voltage wave, and the power factor of the inductive load is also lagging.
Capacitive Load
In the capacitive load, the voltage wave is leading the current wave. The examples of capacitive loads are capacitor bank, three phase induction motor starting circuit, etc. The power factor of such type of loads is leading.
Types of Electrical Loads in Power System
The total loads of an area depend on its population and living standard of the people. The different types of the loads in a power system are as follows.
- Domestic load
- Commercial load
- Industrial load
- Agriculture load
1. Domestic Load – The domestic load is defined as the total energy consumed by the electrical appliances in the household work. It depends on the living standard, weather and type of residence. The domestic loads mainly consist of lights, fan, refrigerator, air conditioners, mixer, grinder, heater, ovens, small pumping, motor, etc. The domestic load consume very little power and also independent from frequency. This load largely consists of lighting, cooling or heating.
2. Commercial Load – Commercial load mainly consist of lightning of shops, offices, advertisements, etc., Fans, Heating, Air conditioning and many other electrical appliances used in establishments such as market restaurants, etc. are considered as a commercial load.
3. Industrial Loads – Industrial load consists of small-scale industries, medium scale industries, large scale industries, heavy industries and cottage industries. The induction motor forms a high proportion of the composite load. The industrial loads are the composite load. The composite load is a function of frequency and voltage and its form a major part of the system load.
4. Agriculture Loads – This type of load is mainly motor pumps-sets load for irrigation purposes. The load factor of this load is very small e.g. 0.15 – 0.20.


good basic principle of loads
Which type of load consumes more power – Inductive or Resistive load?
It is a nice article and just loved this site.