Both bus and star topologies have their own significance in the communicating networks. The crucial difference between bus and star topology is that bus topology uses a single cable through which various peripheral devices are connected. As against a star, topology makes use of a central hub or switch that broadcasts information to all the devices in the network. Bus topology is quite easy to implement in a network. While star topology offers efficient operation.
What is Topology?
Topology is the physical arrangement of various peripheral devices in a network. Basically, we know that multiple devices are connected to a network. When we talk about the way in which various devices are connected, then we call it network topology.
Bus topology is the most basic type of network topology. Whereas star topology is an advanced network orientation. In this article, we will discuss the differentiating factors between bus and star topology.
Content: Bus Vs Star Topology
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Bus Topology | Star Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamental Element | Cable | Hub or switch |
| Speed of data transfer | Slow | Comparatively fast |
| Network orientation | Linear | Non-linear |
| Cost | Low | Quite high |
| Cabling requirement | Less | More |
| Fault detection | Difficult | Comparatively easy |
| Network Extension | This configuration permits addition of many devices. | Here the network permits limited addition of devices. |
| Network Failure | Severe when common cable is hampered. | Severe when the hub malfunctions. |
| Signal Transmission | Unidirectional | It is not unidirectional. |
Definition of Bus Topology
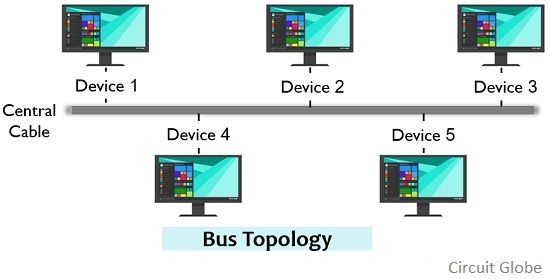
A network configuration in which multiple devices are connected one after the other in a linear manner to a common communication cable is known as bus configuration. The common cable or link can be either coaxial cable or twisted pair cable. The figure below represents the bus topology:
The cable to which various nodes are connected is known as the backbone of the network. This cable serves as the most crucial element of the network, as if it fails then the complete network stops operating. However, bus topology can be easily installed as a single link is required.
It is sometimes called line topology and is generally used in small areas. It does not offer secured communication as the signal is transmitted through a common cable and hence can be accessible to all the devices present in the network. When a device in the network fails, then there is no effect on the other nodes of the network. However, if the cable itself gets failed, then the complete system gets shut down.
Definition of Star Topology
Star topology is a type of network configuration in which various physical devices are individually linked to the hub. This signifies that the device in the network is connected separately to the hub, and there exists no direct interconnection between the multiple devices of the network.
The figure below represents star topology: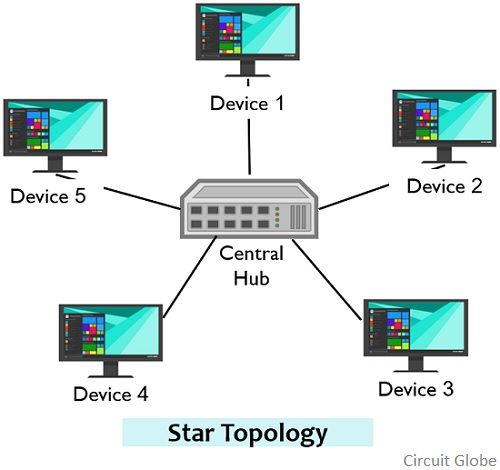
Devices in a star network operate in a way that the central hub through which all the devices are connected broadcasts the data to the respective node from the respective node. Thus, here the signal flow is centrally managed.
This is the reason; the hub must be properly configured as any type of issue in the hub will cause, failure of the complete system. Hence it offers the flexibility of operation with other devices even when a single device of the network is faulty. The whole network configuration resembles a star; thus, it is named so. However, its structure is quite complex, but it is preferred over bus topology due to the advantages associated with it.
Key Differences Between Bus and Star Topology
- The factor that majorly differentiates bus topology from that of star topology is that in bus topology the various devices are connected by a common link or cable and data is transmitted from one node to another through that common cable. While in star topology the multiple devices in the network are connected by the central hub, and it facilitates data sharing.
- When devices are connected in a bus configuration, so data is serially transmitted from one device to another. Thus the speed of data transmission is quite low. Whereas in a star configuration, the hub directly transmits data to the desired peripheral device; hence transmission is quite fast.
- When there is a need for a wide network, then bus topology is preferred. This is so because it supports the easy addition of various devices in the network. While in star topology addition of devices is limited.
- The structure of the bus network is linear as various devices are connected through a straight cable. However, the orientation of the star network is non-linear.
- Only a single common cable is required in bus configuration for any number of devices. While in star network the cable requirement is comparatively more generally equal to the number of devices in the network.
- Star network is expensive in comparison to the bus network.
- Bus topology offers difficult troubleshooting because one has to check all the devices of the linear network to detect the fault. While in star topology fault detection is comparatively easy.
- In bus topology signal is transmitted unidirectionally from one end to another. However, star topology does not follow the same.
Conclusion
Hence from this discussion, we can conclude that the bus is the traditional network orientation but suffers major drawbacks. However, the star is a recent configuration but is more complex.