The most significant difference between the random and the systematic error is that the random error occurs because of the unpredictable disturbances caused by the unknown source or because of the limitation of the instrument. Whereas, the systematic error occurs because of the imperfection of the apparatus. The other differences between the random and the systematic error are represented below in the comparison chart.
The systematic error occurs because of the imperfection of the apparatus. Hence the measured value is either very high or very low as compared to the true value. While in random error the magnitude of error changes in every reading.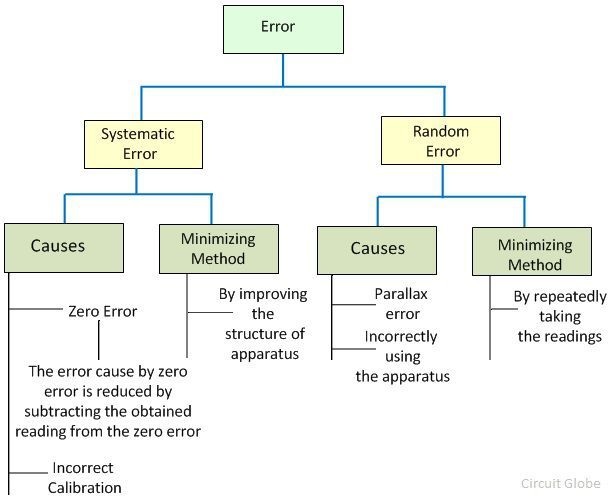
The complete elimination of both the errors cannot be possible. The errors can only be reduced by using the particular methods. The random error reduces by repeatedly taking the readings. And the systematic error reduces by improving the mechanical structure of the apparatus.
Content: Random Vs Systematic Error
Comparison Chart
| Basis For Comparison | Random Error | Systematic Error |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The random error occurs in the experiment because of the uncertain changes in the environment. | It is a constant error which remains same for all the measurements. |
| Causes | Environment, limitation of the instrument, etc. | Incorrect calibration and incorrectly using the apparatus |
| Minimize | By repeatedly taking the reading. | By improving the design of the apparatus. |
| Magnitude of Error | Vary | Constant |
| Direction of Error | Occur in both the direction. | Occur only in one direction. |
| Types | Do not have | Three (Instrument, Environment and systematic error) |
| Reproducible | Non-reproducible | Reproducible |
Definition of Random Error
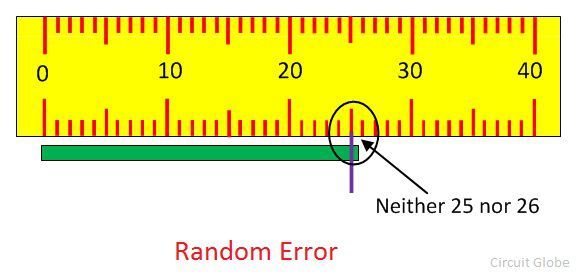
The uncertain disturbances occur in the experiment is known as the random errors. Such type of errors remains in the experiment even after the removal of the systematic error. The magnitude of error varies from one reading to another. The random errors are inconsistent and occur in both the directions.
The presence of random errors is determined only when the different readings are obtained for the measurement of the same quantity under the same condition.
Definition of Systematic Error
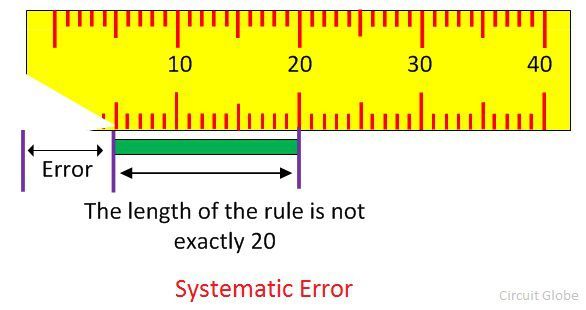
The constant error occurs in the experiment because of the imperfection of the mechanical structure of the apparatus is known as the systematic error. The systematic errors arise because of the incorrect calibration of the device.
The error is mainly categorised into three types.
- Instrumental Error
- Environmental Error
- Observational Error
Instrumental Error – The instrumental error occurs because of the three reasons.
- Misuse of the apparatus.
- Imperfection in the mechanical structure of the apparatus.
- The error occurs because of the loading effect.
Observational Error – The error occurs in the observation of the reading is known as the observational error. For example, consider the pointer of voltmeter rest on the surface of the scale. The observational error occurs in the reading if the line of vision is exactly not above the pointer.
Environmental Error – Such types of error occurs because of the changes in the surroundings condition like humidity, pressure, magnetic or electrostatic field, etc. The experimental errors can be reduced by making some arrangements in the laboratory for controlling the temperature and humidity. Also, before experimenting make ensure that there should be no magnetic and electric field.
Key Differences between the Random & Systematic Error
The following are the major differences between the systematic and random error.
- The random error means the unpredictable disturbance occurs in the experiment by the unknown source. Whereas, the systematic error occurs because of the inbuilt defect of the apparatus.
- The random error occurs in both the direction, whereas the systematic error occurs only in one direction. The systematic errors arise because of the inbuilt fault of the apparatus, hence it always gives the same error. The random error occurs because of the unknown source, thereby occurs in any direction.
- The magnitude of systematic error remains constant because the defect is inbuilt inside the apparatus. Whereas, the magnitude of the random error is variable.
- The zero error and the incorrect calibration of apparatus cause the systematic error. The random error is because of the parallax or by incorrectly using the apparatus.
- The random error reduces by taking the two or more readings of the same experiment, whereas the systematic error reduces by carefully designing the apparatus.
- The random error does not have any specific types, whereas the systematic error is categorised into three types, i.e., instrument error, environment error and systematic error.
- The random error is non-reproducible whereas the systematic error is reproducible because the defect is inbuilt with the apparatus.
Conclusion
The random error happens because of any disturbances occurs in the surrounding like the variation in temperature, pressure or because of the observer who takes the wrong reading. The systematic error arises because of the mechanical structure of the apparatus. The complete elimination of both the error is impossible.

Gud one