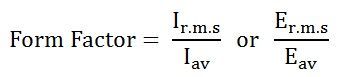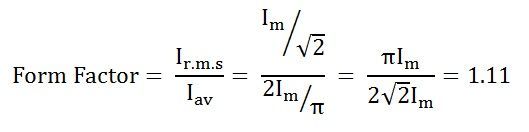Definition: The ratio of the root mean square value to the average value of an alternating quantity (current or voltage) is called Form Factor. The average of all the instantaneous values of current and voltage over one complete cycle is known as the average value of the alternating quantities.
Mathematically, it is expressed as:
Ir.m.s and Er.m.s are the roots mean square values of the current and the voltage respectively, and Iav and Eav are the average values of the alternating current and the voltage respectively.
For the current varying sinusoidally, the Form Factor is given as:
The value of Form Factor is 1.11
There is a relation between the peak value, the average value, and the root means square (R.M.S) value of an alternating quantity. Therefore, to express the relationship between all these three quantities, the two factors are used, namely as Peak Factor and Form Factor.
The Form Factor for the various sinusoidal waveforms are as follows:
- For a sine wave, it is π/2√2 = 1.11072073
- For a half-wave rectified sine wave, it is π/2 = 1.5707963
- For a full-wave rectified sine wave, it is π/2√2 = 1.11072073
- For a square wave, it is equal to 1
- For triangle waveform, it is 2/√3 = 1.15470054
- For sawtooth waveform, it is 2/√3 = 1.15470054
This is all about the form factor.